Create an app¶
In this section we are looking how to make an interactive application using Pymunk.
class App:
"""Create a single-window app with multiple spaces (scenes)."""
spaces = []
current = None
size = 640, 240
def __init__(self):
"""Initialize pygame and the app."""
pygame.init()
self.screen = pygame.display.set_mode(App.size)
self.running = True
self.stepping = True
self.rect = Rect((0, 0), App.size)
self.draw_options = pymunk.pygame_util.DrawOptions(self.screen)
self.dt = 1/50
self.shortcuts = {
K_a: 'Arrow(get_mouse_pos(self.screen), color=BLACK)',
K_b: 'Rectangle(get_mouse_pos(self.screen), color=GREEN)',
K_v: 'Rectangle(get_mouse_pos(self.screen), color=BLUE)',
K_c: 'Circle(get_mouse_pos(self.screen), color=RED)',
K_n: 'self.next_space()',
K_q: 'self.running = False',
K_ESCAPE: 'self.running = False',
K_SPACE: 'self.stepping = not self.stepping',
K_1: 'self.draw_options.flags ^= 1',
K_2: 'self.draw_options.flags ^= 2',
K_3: 'self.draw_options.flags ^= 4',
K_p: 'self.capture()',
K_s: 'App.current.space.step(self.dt)',
K_z: 'App.current.remove_all()',
K_g: 'App.current.space.gravity = 0, 0',
}
def run(self):
"""Run the main event loop."""
while self.running:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
self.running = False
elif event.type == KEYDOWN:
self.do_shortcut(event)
App.current.do_event(event)
for s in App.current.space.shapes:
if s.body.position.y < -100:
App.current.space.remove(s)
self.draw()
if self.stepping:
App.current.space.step(self.dt)
pygame.quit()
def draw(self):
self.screen.fill(App.current.color)
for obj in App.current.objects:
obj.draw()
App.current.space.debug_draw(self.draw_options)
self.draw_cg()
App.current.draw()
rect = App.current.sel_rect
pygame.draw.rect(self.screen, GREEN, rect, 1)
pygame.display.update()
def draw_cg(self):
"""Draw the center of gravity."""
screen = pygame.display.get_surface()
for b in App.current.space.bodies:
cg = b.position + b.center_of_gravity
p = to_pygame(cg, screen)
pygame.draw.circle(screen, BLUE, p, 5, 1)
def do_shortcut(self, event):
"""Find the key/mod combination and execute the cmd."""
k = event.key
m = event.mod
cmd = ''
if k in self.shortcuts:
cmd = self.shortcuts[k]
elif (k, m) in self.shortcuts:
cmd = self.shortcuts[k, m]
if cmd != '':
try:
exec(cmd)
except:
print(f'cmd error: <{cmd}>')
def next_space(self):
d = 1
if pygame.key.get_mods() & KMOD_SHIFT:
d = -1
n = len(App.spaces)
i = App.spaces.index(App.current)
i = (i+d) % n
App.current = App.spaces[i]
pygame.display.set_caption(App.current.caption)
for s in App.current.space.shapes:
print(s, s.bb)
def draw_positions(self):
for body in App.current.space.bodies:
print(body.mass)
def capture(self):
"""Save a screen capture to the directory of the calling class"""
name = type(self).__name__
module = sys.modules['__main__']
path, name = os.path.split(module.__file__)
name, ext = os.path.splitext(name)
filename = path + '/' + name + '.png'
pygame.image.save(self.screen, filename)
Circle¶
The Circle class creates a body with an attached circle shape.
class Circle:
def __init__(self, p0, radius=10, color=None):
self.body = pymunk.Body()
self.body.position = p0
shape = pymunk.Circle(self.body, radius)
shape.density = 0.01
shape.elasticity = 0.5
shape.friction = 0.5
if color != None:
shape.color = color
App.current.space.add(self.body, shape)
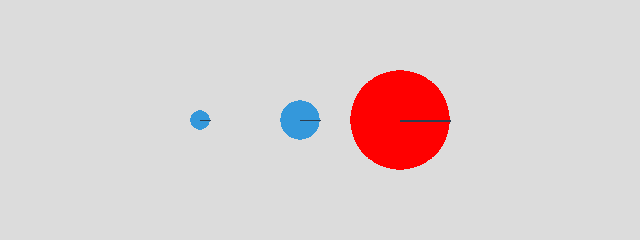
This is an exemple of three circles placed in a no-gravity space:
p0 = Vec2d(200, 120)
v = Vec2d(100, 0)
Space('Cercle', GRAY, gravity=(0, 0))
Circle(p0)
Circle(p0+v, 20)
Circle(p0+2*v, 50, RED)
Segment¶
The Segment class creates a linear segment starting at position p0
having a direction vector v, a radius and a color.
class Segment:
def __init__(self, p0, v, radius=10, color=None):
self.body = pymunk.Body()
self.body.position = p0
shape = pymunk.Segment(self.body, (0, 0), v, radius)
shape.density = 0.01
shape.elasticity = 0.5
shape.friction = 0.5
if color != None:
shape.color = color
App.current.space.add(self.body, shape)
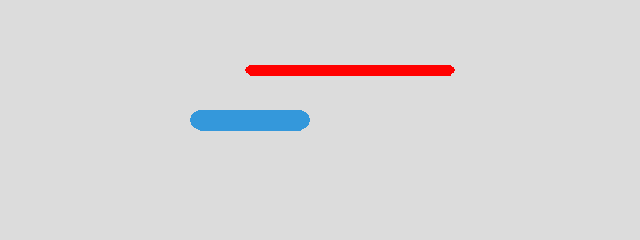
This is an example of two segments of different radius, length and color:
Space('Segment', gravity=(0, 0))
Segment(p0, v)
Segment(p0+(50, 50), 2*v, 5, RED)
Poly¶
The Poly class creates a filled polygon placed at position p0
with the vertices v given with a vertex list.
class Poly:
def __init__(self, p0, vertices, color=None):
self.body = pymunk.Body()
self.body.position = p0
self.shape = pymunk.Poly(self.body, vertices)
self.shape.density = 0.01
self.shape.elasticity = 0.5
self.shape.friction = 0.5
if color != None:
self.shape.color = color
App.current.space.add(self.body, self.shape)
This is an example of creating a triangle and a square polygon:
Space('Poly', gravity=(0, 0))
triangle = [(-30, -30), (30, -30), (0, 30)]
Poly(p0, triangle)
square = [(-30, -30), (30, -30), (30, 30), (-30, 30)]
Poly(p0+v, square)
